How to Choose the Right IMU for UAVs?

UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) typically use tactical-grade or industrial-grade IMUs depending on their application. Tactical-grade IMUs provide higher precision and stability, essential for military drones or those requiring accurate long-term navigation. In contrast, industrial-grade IMUs are more suited for commercial drones, offering a balance between cost and performance. Both types measure orientation, acceleration, and angular velocity to ensure stable flight and precise navigation in varying conditions.
What is a MEMS IMU?
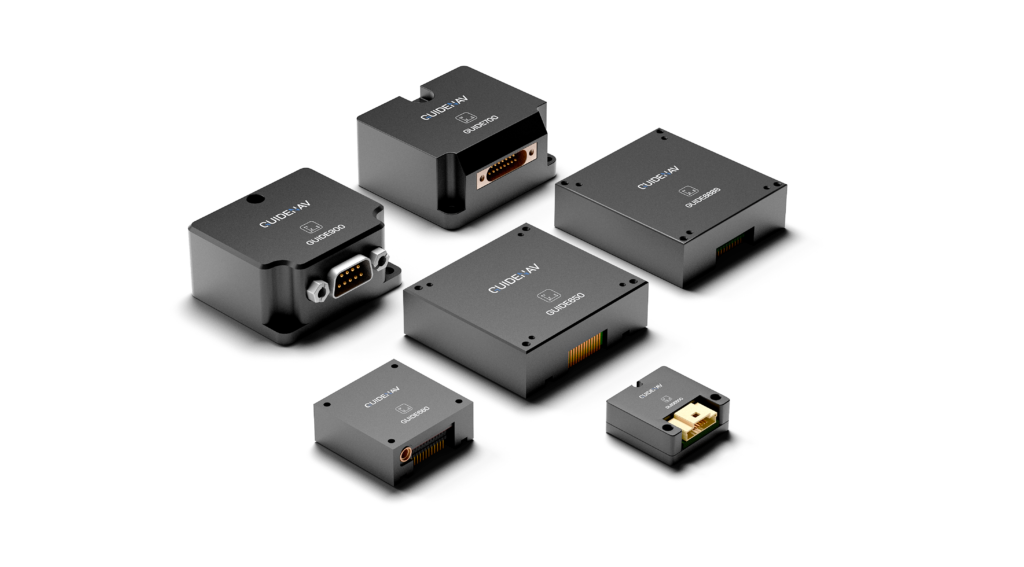

A MEMS IMU (Micro-Electro-Mechanical System Inertial Measurement Unit) combines accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sometimes magnetometers into a single device to measure motion and orientation. These tiny yet powerful units provide crucial data in countless applications, from drones to industrial robots, making them indispensable for businesses aiming to integrate precise navigation and control into their systems.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs)?

IMUs, or Inertial Measurement Units, are essential devices that measure acceleration, angular rate, and sometimes the magnetic field around them. This enables them to track orientation, velocity, and movement without depending on external signals like GPS. In industries ranging from aerospace to autonomous driving, IMUs are indispensable for navigating challenging environments.
The Ultimate Guide to Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)

An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is a sensor system that measures acceleration, angular velocity, and often magnetic fields to determine an object’s orientation and movement in space. It typically includes accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sometimes magnetometers. These components work together to provide crucial data for navigation, stabilization, and control in a wide range of applications, from aerospace and robotics to smartphones and autonomous vehicles. IMUs are essential in systems where precise movement and orientation data are required.
What is a Fiber Optic Gyroscope?
A Fiber Optic Gyroscope (FOG) measures an object’s rotation using the interference of light in coiled fiber optics. The result is highly accurate data about orientation, crucial for navigation and stabilization across fields like aerospace, defense, and maritime operations. It’s a piece of tech you’ll find in systems that simply cannot afford to fail.
What is the Primary Function of the Inertial Measurement Unit?

The primary function of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is to measure and report an object’s acceleration, angular velocity, and orientation, ensuring accurate navigation and motion control. IMUs are essential in industries such as aerospace, defense, and robotics, where precision is non-negotiable.
What is an IMU? Understanding Inertial Measurement Units

An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is an advanced electronic device that measures and reports an object’s acceleration, angular rate, and orientation. It consists of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and often magnetometers, providing crucial data for navigation, control systems, and stabilization.
