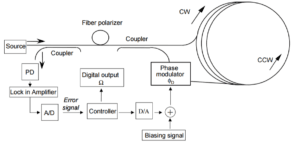
Open-Loop or Closed-Loop FOG? Understanding the Difference
Open-loop FOGs are compact and cost-effective, with medium accuracy (1–10 °/h) for UAVs and robots. Closed-loop FOGs deliver ultra-high precision (0.001–0.1 °/h), making them essential in submarines, missiles, and aerospace systems.

Top 10 MEMS INS Suppliers in 2025
The top 10 MEMS INS suppliers in 2025 include Honeywell, Analog Devices, GuideNav, Safran, TDK InvenSense, STMicroelectronics, Sensonor, Silicon Sensing Systems, Aceinna, and SBG Systems.

FOG vs MEMS in Subsea Navigation: Which One Holds Better? (Part II)
FOG gyroscopes maintain ultra-low drift and long-term stability under GNSS-denied subsea conditions, while MEMS IMUs offer compact, low-power alternatives better suited for short-duration inspections and cost-sensitive platforms.

FOG vs MEMS in Subsea Navigation: Which One Holds Better? (Part I)
FOG gyroscopes maintain ultra-low drift and long-term stability under GNSS-denied subsea conditions, while MEMS IMUs offer compact, low-power alternatives better suited for short-duration inspections and cost-sensitive platforms.

FOG vs RLG: Evaluating Accuracy, Reliability, and Lifecycle Costs
FOG and RLG are both established gyroscope technologies for defense navigation. But when buyers compare them through the lens of procurement, FOG delivers the optimal balance of performance, reliability, and lifecycle cost for nearly every mission outside of strategic deterrence.
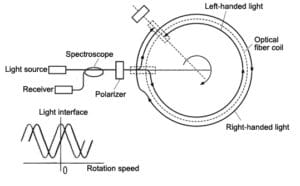
How to Choose a FOG That Integrates, Performs, and Supports You
Selecting the wrong Fiber Optic Gyroscope (FOG) can delay projects and raise costs. Smart buyers look beyond the datasheet-choosing a FOG that integrates smoothly, performs consistently, and comes with guaranteed long-term service and delivery assurance.
