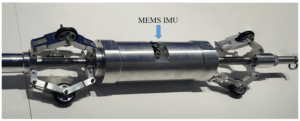
Application of MEMS IMU in Pipeline Inspection Robots
MEMS IMUs deliver precise inertial navigation for pipeline inspection robots operating in GNSS-denied environments. By providing stable attitude, velocity, and position data, they ensure reliable defect mapping, smooth trajectory control, and continuous operation in confined underground or subsea pipelines.

The Hidden Traps in Using High-Precision MEMS IMUs: What Every Integrator Should Know
High-precision MEMS IMUs deliver unmatched motion sensing performance — but only if used correctly. This reveals four critical usage mistakes that often cause accuracy loss, and how to prevent them in real-world integration.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Honeywell MEMS IMU HG1930
The Honeywell HG1930 is a compact, tactical-grade MEMS IMU offering reliable performance and rugged design for UAVs, robotics, and defense systems. It delivers stable accuracy in harsh environments but comes with higher cost and export limitations.

Inside the INS-Based Localization Technology Behind Autonomous Driving
Autonomous vehicles achieve centimeter-level accuracy through GNSS/INS integration, LiDAR mapping, and visual perception, with high-precision IMUs forming the core of localization when GPS signals fail.

Can an IMU Alone Perform Odometry?
An IMU can theoretically compute odometry through double integration, but bias and noise make it drift exponentially over time. Real-world navigation systems therefore rely on IMU fusion with GNSS, LiDAR, or cameras to maintain precision and stability.
When Should You Recalibrate or Replace a FOG IMU?
Recalibrate your FOG IMU every 12–24 months to maintain bias stability. Replace it after 5–8 years or when drift exceeds specifications to ensure long-term navigation reliability.
