NMEA (National Marine Electronics Association) is a standardized data format used for communication between navigation devices, including GNSS receivers, inertial navigation systems (INS), and maritime electronics. The NMEA 0183 and NMEA 2000 protocols define how navigation data, such as position, speed, heading, and time, is transmitted and shared across different systems.
How NMEA is Used in INS?
Data Exchange Between INS & GNSS – NMEA messages allow INS to receive GNSS updates for error correction.
Integration with External Systems – Used in maritime, aviation, and automotive applications for seamless navigation data sharing.
Supports Multiple Navigation Parameters – Transmits latitude, longitude, altitude, speed, and heading.
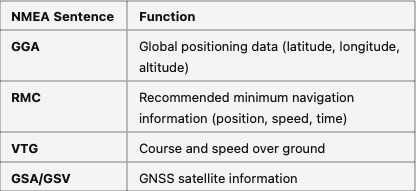
Common NMEA Sentences in INS
Applications of NMEA in INS
✔ Maritime & Submarine Navigation – Ensures standardized data transmission between INS and navigation displays.
✔ Aerospace & Aviation – Used for flight management systems and avionics.
✔ Autonomous Vehicles & Robotics – Supports sensor fusion in self-driving cars and UAVs.
Advantages of NMEA in INS
✔ Interoperability – Works across different navigation and positioning systems.
✔ Lightweight & Efficient Data Transmission – Uses compact ASCII messages for real-time updates.
✔ Industry Standard for Navigation – Widely adopted in GNSS, INS, and marine electronics.
