FOG (Fiber Optic Gyroscope) is a high-precision gyroscope technology used in Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) to measure angular velocity without any moving parts. FOG-based INS is widely used in aerospace, defense, marine, and autonomous navigation systems due to its high accuracy, low drift, and immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI).
How Does FOG Work?
Light Travels Through Optical Fiber – A laser beam is split into two and sent in opposite directions through a coiled optical fiber.
Sagnac Effect Measures Rotation – When the system rotates, the interference pattern of the light waves changes, allowing precise angular velocity measurement.
INS Uses FOG Data – The angular velocity is integrated to determine orientation, position, and motion.
Advantages of FOG in INS
✔ High Accuracy & Low Drift – Suitable for long-duration navigation without GNSS assistance.
✔ No Moving Parts – More durable and reliable compared to mechanical gyroscopes.
✔ Immune to EMI & Magnetic Fields – Ideal for military and aerospace applications.
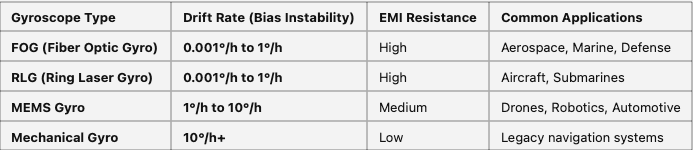
FOG vs. Other Gyroscope Technologies