The term course in navigation refers to the intended direction of travel or the path along which a vehicle, vessel, or aircraft is headed, usually expressed in terms of an angle or bearing relative to a fixed reference (like true north or magnetic north).
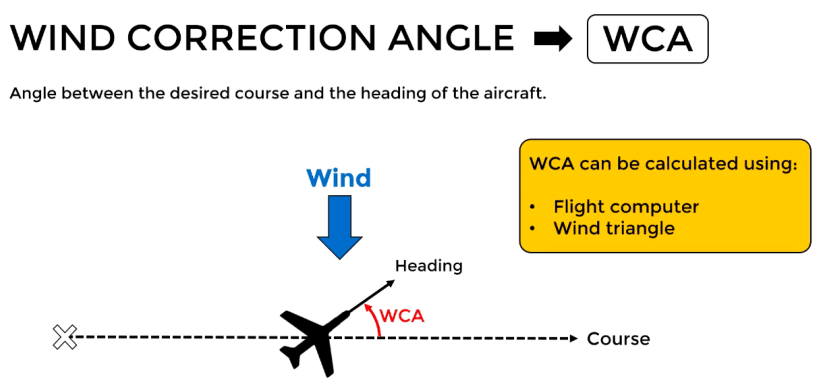
Key Points:
1. Course vs. Heading:
- Course is the planned direction of travel, typically the desired path over the ground or water.
- Heading refers to the actual direction in which the vessel or vehicle is pointing at any given time. The heading can differ from the course due to factors like wind, current, or steering errors.
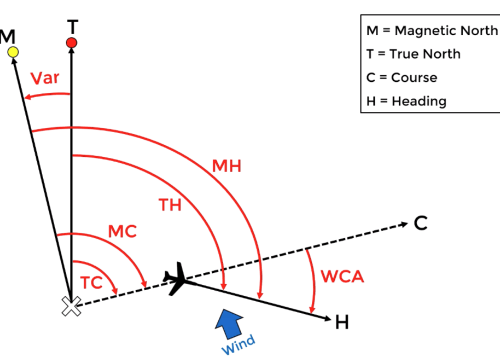
2. Measurement:
- Course is typically measured in degrees from 0° to 360°, with 0° or 360° representing true north.
- For example, a course of 90° would mean traveling east, 180° would mean traveling south, and 270° would be traveling west.
3. Course Over Ground (COG):
- COG is the actual direction of movement over the Earth’s surface. It can differ from the course due to external factors like wind or current, especially in maritime or aviation contexts.
4. Use in Different Domains:
- Aviation: The course is the planned flight path, often specified in waypoints or airways.
- Maritime: The course is the direction a ship or boat should follow over the water.
- Land Navigation: The course indicates the direction in which a person or vehicle should travel to reach a destination.
In short, the course is the intended direction of movement, while heading refers to the direction in which the object is actually pointing.
