After working with inertial sensors for over a decade, I’ve seen firsthand how quickly system requirements evolve. A few years ago, a 6-axis IMU—just gyroscopes and accelerometers—was enough for most navigation and control tasks. But that’s no longer the case. Today’s platforms demand more than just motion—they need orientation, altitude, and environmental awareness. That’s why 10-axis MEMS IMUs have become my go-to for complex applications. By adding a magnetometer and a barometric sensor, we gain two extra data dimensions: absolute heading and vertical positioning. These aren’t just numbers—they’re what enable stable control in GNSS-denied zones, accurate indoor localization, and precision in multi-layered environments. The more data we have, the more problems we can solve.
A 10-axis MEMS IMU offers a significant leap over traditional 3-axis or 6-axis sensors by combining gyroscopes, accelerometers, magnetometers, and a barometer into one compact module. This richer sensor fusion enables not only motion tracking, but also absolute heading and altitude awareness–crucial for reliable navigation, control, and stability in complex or GPS-denied environments.
Want to know how each sensor works—and why they matter? Let’s break down all the components.
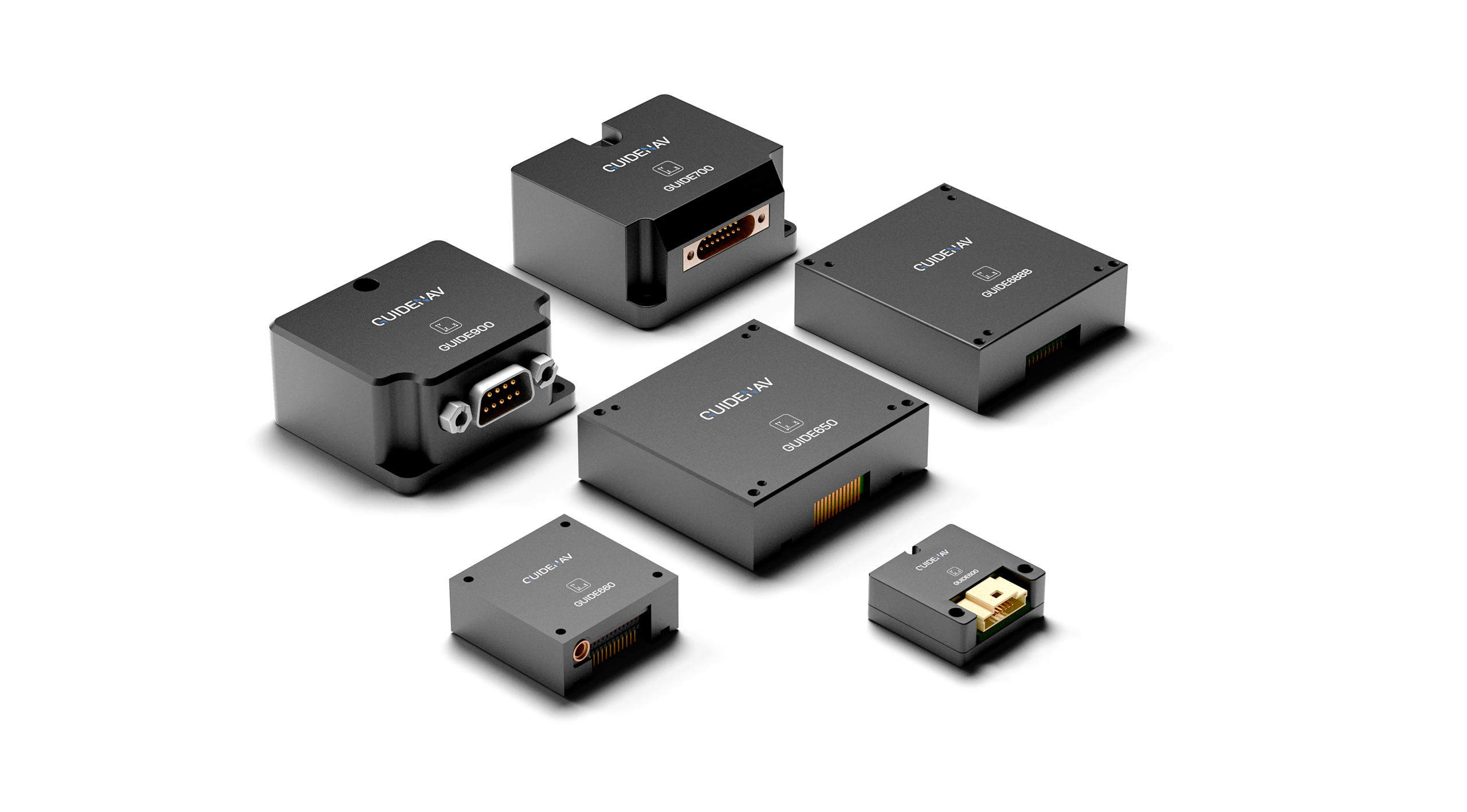

Table of contents
What Does “10-Axis” Really Mean?
In industry terms, a 10-axis MEMS IMU typically combines four sensor types in a single compact module:
- 3-axis gyroscopesfor rotational motion
- 3-axis accelerometersfor linear acceleration and tilt
- 3-axis magnetometersfor absolute heading
- 1-axis barometric pressure sensorfor altitude estimation
This combination delivers a full 10 degrees of inertial and environmental sensing, giving engineers access to a richer, more complete picture of platform motion and spatial orientation—especially in GNSS-challenged environments.
Gyroscope–Angular Velocity at the Core of 10-Axis MEMS IMUs
The gyroscope is the foundation of any 10-axis MEMS IMU, providing precise angular velocity data along the X, Y, and Z axes. It enables real-time attitude estimation and stabilization for fast-moving platforms. In tactical-grade systems, low drift and high responsiveness are essential.
Key Parameters:
| Sensor | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Gyroscope | Angular range | Measures full 3-axis rotational motion |
| Bias instability | Supports long-term drift correction | |
| Noise performance | Enables smooth, jitter-free tracking | |
| Bandwidth & output rate | High-frequency data for fast response |
Accelerometer–Linear Motion and Vibration Sensing for Precision Navigation
The accelerometer in a 10-axis IMU captures both dynamic acceleration and static gravitational forces along three axes. This enables accurate sensing of movement, vibration, and tilt orientation, especially important in dead reckoning or GNSS-denied conditions.
Key Parameters:
| Sensor | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Accelerometer | Acceleration range | Detects shock, motion, and tilt |
| Bias instability | Enables high-resolution inertial sensing | |
| Noise floor | Reduces false movement triggers | |
| Bandwidth & response | Suitable for high-dynamic environments |
Magnetometer–Absolute Heading for Long-Term Orientation Correction
The magnetometer complements gyroscopic sensing by offering a stable reference to Earth’s magnetic field—essential for heading estimation over long missions. It helps correct drift and enables reliable directional awareness, especially in indoor or GPS-compromised environments.
Key Parameters:
| Sensor | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetometer | Magnetic field range | Covers a wide operating environment |
| Resolution | Captures small heading changes accurately | |
| Noise characteristics | Supports consistent orientation correction |
Barometer–Vertical Awareness for 3D Navigation
The barometric pressure sensor gives a 10-axis MEMS IMU vertical awareness, translating air pressure into altitude estimation. This is essential for indoor UAVs, VTOL platforms, and smart robotics where GNSS elevation data may be unavailable.
Key Parameters:
| Sensor | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Barometer | Pressure range | Enables wide-altitude operational scenarios |
| Resolution | Detects small changes in elevation | |
| Measurement stability | Ensures consistent Z-axis positioning |
Why 10-Axis IMUs Make a Difference in Real-World Applications?
While 3-axis or 6-axis IMUs can capture basic motion and orientation, they often fall short in complex, GNSS-challenged environments. A 10-axis MEMS IMU integrates gyroscope, accelerometer, magnetometer, and barometer sensors—offering a more complete understanding of both motion and environment.
This richer data enables:
- Absolute heading correctionthrough magnetic field sensing
- Vertical position awarenessvia air pressure measurement
- Improved dead reckoningin GPS-denied or indoor conditions
- Greater robustness against drift, vibration, and system noise
For platforms that need to think, react, and navigate independently, 10-axis sensing provides the extra dimensions that standard IMUs simply can’t cover.
How Do You Know If You Really Need a 10-Axis IMU?
Not every project requires a full 10-axis IMU—but if your application involves GPS-denied environments, vertical mobility, or long-duration heading stability, then a 10-axis system could be essential.
You should consider choosing a 10-axis MEMS IMU if:
- You need absolute heading (not just relative rotation)
- Your platform must operate indoors, underground, or in GNSS-degraded areas
- You require altitude estimation or multi-floor navigation
- Your system drifts over time using only gyro + accelerometer
- You want to enable true 3D spatial awareness from a single sensor module
If any of the above applies, upgrading from 6-axis to 10-axis is not overengineering—it’s mission assurance.

Where Are 10-Axis IMUs Most Commonly Used?
10-axis IMUs aren’t just for specialized systems—they’ve become essential in many modern platforms where motion, orientation, and environmental awareness must work together. So, in which applications are they used most often?
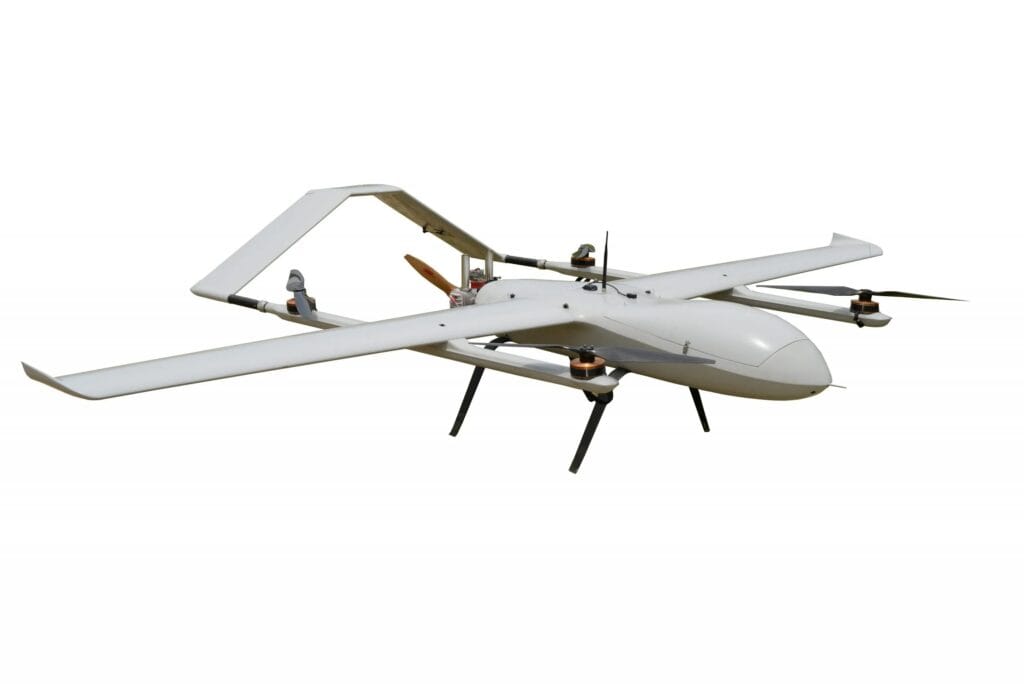
1.Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
A 10-axis IMU allows UAVs to hold altitude with barometric data, correct heading drift using a magnetometer, and maintain control in GNSS outages or cluttered airspace. This is essential for autonomous flight, VTOL stabilization, and safe return-to-home features under degraded navigation conditions.
2.Ground Robots and UGVs
In tunnels, basements, or GPS-denied facilities, UGVs rely on inertial systems to navigate. With a 10-axis IMU, robots gain vertical awareness and heading correction—allowing them to traverse floors, ramps, or complex turns with greater positional accuracy, even in the absence of mapping infrastructure.
3.Precision-Guided Systems and Munitions
Compact, high-shock applications like smart munitions benefit from full 10-axis feedback: gyros for orientation, accelerometers for acceleration, magnetometers for course correction, and barometers for altitude profiling. This enables precise targeting, adaptive control, and stable guidance through GNSS loss or countermeasures.
4.Gimbals and Optical Payloads
For stabilized optics, IMU drift can degrade pointing accuracy over time. 10-axis IMUs use magnetometers for azimuth correction and barometers for tilt/elevation reference—keeping cameras or sensors locked on target with pixel-level precision, even on unstable or moving platforms.
5.Indoor Navigation and Smart Mobility
Whether on delivery robots, AR headsets, or wearable trackers, 10-axis IMUs support full orientation and 3D motion tracking indoors. Barometers detect elevation changes between floors, while magnetometers provide orientation cues in steel-framed environments—making indoor navigation more precise and reliable without beacons or GNSS.
GuideNav’s 10-Axis IMU: Built for Integration
At GuideNav, our 10-axis MEMS IMUs combine a tactical-grade 6-axis core with integrated magnetometer and barometer—offering full-state sensing for GNSS-denied, dynamic environments. Each unit is calibrated across temperature and aligned for real-world deployment, not just lab tests.
We support deep customization—output filtering, bandwidth tuning, interface adaptation, or structural adjustments—to match your platform requirements.
What sets us apart isn’t just the sensor specs, but how we work:
- Engineering support from prototyping to rollout
- Customizable interfaces and connectors tailored to your platform
- Stable production with lifecycle continuity
- Export-friendly, ITAR-free availability
If your system depends on reliable orientation and altitude awareness, our 10-axis IMUs are ready for integration.
