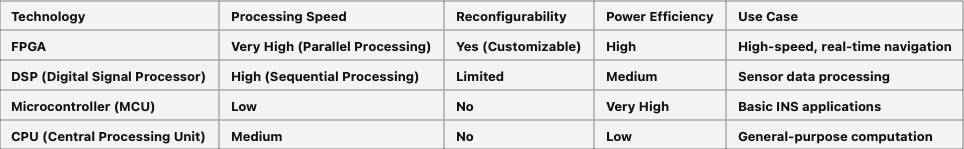
FPGA (alan programlanabilir kapı dizisi), gerçek zamanlı sensör veri işleme, filtreleme ve füzyonu işlemek için Atalet Navigasyon Sistemlerinde (INS) kullanılan bir dijital işleme çipidir . yüksek hızlı hesaplama, düşük gecikme ve paralel işleme sunar , bu da onları havacılık, savunma, robotik ve otonom araçlarda hassas navigasyon uygulamaları .
INS'de FPGA nasıl kullanılır?
Gerçek zamanlı sensör füzyonu doğru konumlandırma için IMU (jiroskop ve ivmeölçer) verilerini, GNSS sinyallerini ve harici sensörleri birleştirir
Kalman Filtreleme - Ins.
Yüksek hızlı paralel işleme aynı anda birden fazla navigasyon hesaplamasını işler ve sistem duyarlılığını artırır.
Özelleştirilebilir algoritmalar - kullanıcıların gezinme filtrelerini, iletişim protokollerini ve veri füzyon tekniklerini .
Ataletal navigasyonda FPGA'nın avantajları
✔ Ultra hızlı işleme Füzeler, İHA ve denizaltılar gibi yüksek dinamik navigasyon için idealdir .
✔ Düşük gecikme gerçek zamanlı veri işleme sağlar , gezinme hatalarını azaltır.
✔ Yeniden yapılandırılabilir donanım - özelleştirilmiş gezinme algoritmaları için ürün yazılımı güncellemelerine .
✔ Enerji verimli aynı hesaplama görevleri için geleneksel mikroişlemcilere kıyasla daha az güç tüketir
FPGA ve INS'de diğer işleme teknolojileri