In today’s fast-paced world of technology, having a reliable and accurate navigation system is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re in the defense, aerospace, or industrial sectors, precise positioning can make or break your operations. That’s where the Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) becomes a game-changer.
An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is an advanced electronic device that measures and reports an object’s acceleration, angular rate, and orientation. It consists of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and often magnetometers, providing crucial data for navigation, control systems, and stabilization.
But why does IMU play such an important role in modern tech applications? This article will outline the IMU from a series of basic perspectives so you can begin to understand it. Let’s get started.
Table of contents
What Are the Main Components of an IMU?
Gyroscopes: Measure angular velocity(how fast you are rotating about one or more axes).
Accelerometers: Measure linear acceleration along one or more axes. This helps you figure out how fast you’re speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction.
Magnetometers: Sometimes included in IMUs, magnetometers measure the strength and direction of the magnetic field.
This helps you figure out your orientation relative to the Earth’s magnetic field.
How Does an IMU Work? What is IMU Data Used For?
At its core, an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is made up of three accelerometers and three gyroscopes, working together to measure acceleration and angular velocity across the X, Y, and Z axes. Some advanced models even include magnetometers, which detect magnetic fields to help you figure out your orientation relative to Earth’s magnetic field. With these sensors, the IMU is then able to create a full 3D picture of an object’s motion and orientation.
In simple terms, the IMU takes the inertia it senses and turns it into data that describes how the object is moving. That data is then fed into other systems, such as vehicle control systems, to help maintain smooth navigation and precise control. For example, in drones, the IMU is constantly checking changes in orientation and speed, making sure the drone stays stable and on the right path.

How accurate is the IMU?
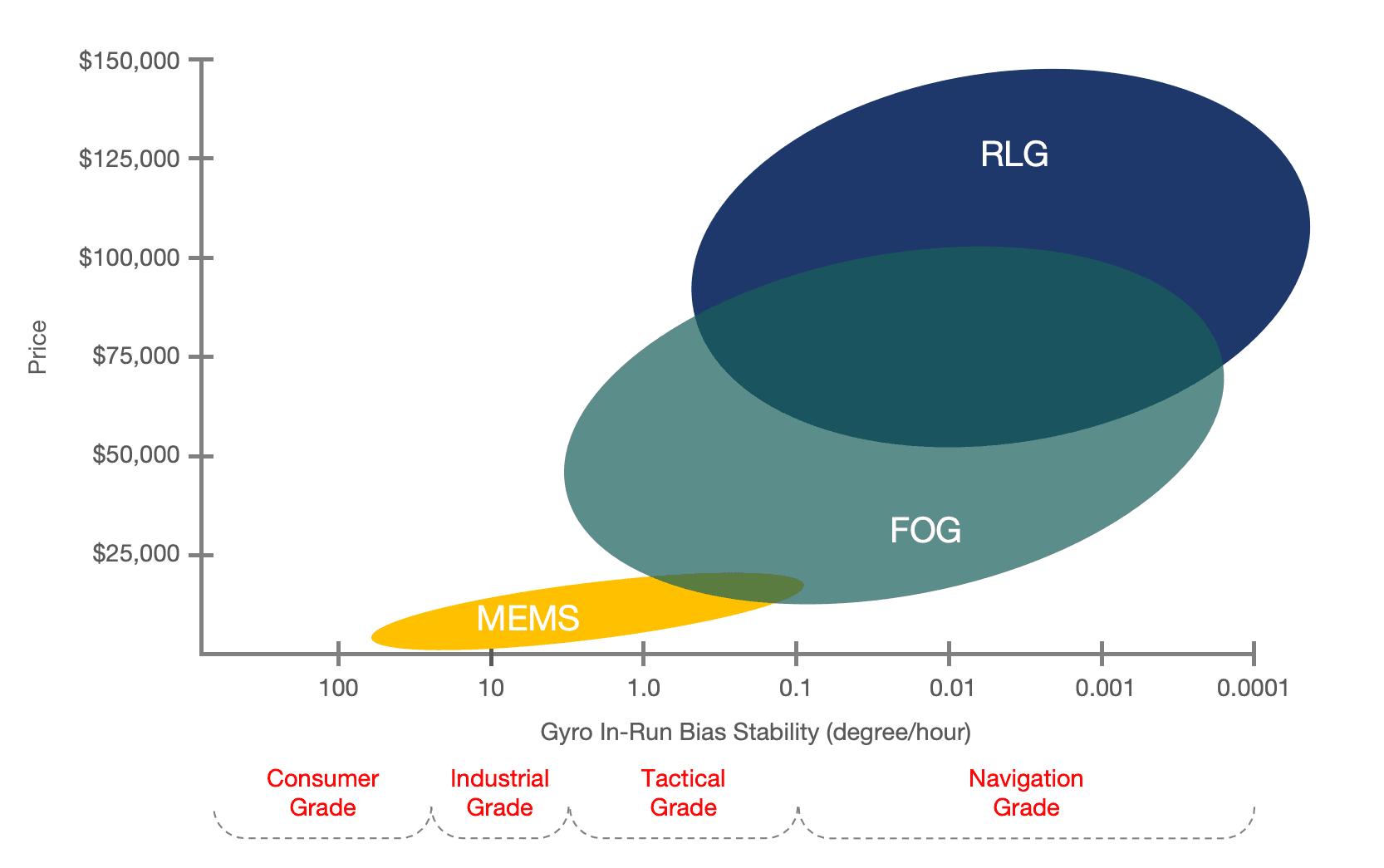
The accuracy of Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) can vary a lot depending on their type and grade. One of the easiest ways to gauge an IMU’s accuracy is by looking at its “bias instability”—a measure of how stable the gyroscope’s readings are over time. Based on this, IMUs are generally classified into four main levels. Here’s a quick overview of common IMU types and their accuracy ranges:
Consumer-Grade IMUs:
- Consumer-Grade IMUs:
- Gyroscope Bias Instability: Typically ranges from 10 to 100 degrees per hour.
- Applications: Mobile phones, gaming controllers, motion tracking devices.
- Industrial-Grade IMUs:
- Gyroscope Bias Instability: Generally about 0.1 to 10 degrees per hour.
- Applications: Drones, robotic navigation, automotive sensors.
- Tactical-Grade IMUs:
- Gyroscope Bias Instability: Ranges from 0.01 to 1 degree per hour.
- Applications: Advanced drone systems, military equipment, research-level measurement tools.
- Navigation-Grade IMUs:
- Gyroscope Bias Instability: Less than 0.01 degrees per hour.
- Applications: Aerospace, deep-sea exploration, advanced navigation systems.
Different levels of IMUs come with varying degrees of accuracy and are used for different applications. As you’d expect, the higher the precision, the steeper the price tag. However, the payoff is more reliable data, especially in high-risk situations where precision is critical.
What is the IMU on a Drone?
Now, let’s talk about how IMUs work with drones. In short, it measures and tells you the attitude of the aircraft (roll, pitch, and yaw), the velocity of the aircraft, changes in altitude, and gravitational forces. This information helps the drone stay on the course you’ve set, even when it experiences outside forces like wind or sudden maneuvers.
What Are the Applications of IMUs?
IMUs are used in various applications where accurate motion tracking is essential:
- Aerospace: In aircraft and spacecraft for navigation and stabilization.
- Autonomous Vehicles: For precise positioning and orientation.
- Mobile Devices: In smartphones and tablets for motion sensing and screen orientation.
- Virtual Reality: To track head movements and enhance the immersive experience.
- Robotics: For guidance and stabilization of robotics.
Applications of IMUs in the Defense Industry
In the defense industry, IMUs are absolutely critical. They’re used in all sorts of things like missile guidance, navigation of vehicles, and stabilizing weapon platforms. The data from an IMU is crucial to keep things accurate and reliable in these high-stakes environments. For buyers from the defense sectors, who are buying IMUs to put into their systems, the quality and the accuracy of the IMU can directly determine whether they are successful in their mission or not.

How much does an IMU cost?
The price of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) can range from a few dollars to thousands of dollars depending on the type, precision, and applications. The general pricing of IMUs based on grades is as follows:
Consumer-Grade IMUs: These are the most affordable types. They typically cost from a few dollars up to around $50. These devices offer basic functionality with moderate accuracy and are suitable for commercial applications.
Industrial-Grade IMUs: Used in applications like drones, automotive sensors, and industrial machinery. Prices range from about $100 to a few thousand dollars, depending on the specific requirements for accuracy.
Tactical-Grade IMUs: They come with higher accuracy, such as advanced drones, and military equipment, and cost from several thousand dollars to over $10,000.
Navigation-Grade IMUs: The most precise and expensive type. You can see them in aerospace, and high-end applications that need super-high accuracy. Navigation-grade IMUs typically cost tens of thousands of dollars, and prices can even reach the hundreds of thousands for those top models.
Customization and Quality: Why Choose Guidenav’s IMUs?
We at Guidenav, understand that every project is different. That’s why we provide custom IMU solutions tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you need more precision, greater durability, or integration into a complex system, our team is on hand to furnish you with a precision-engineered IMU designed specifically for your operational needs. With 19 years of experience and a record of previous success in the defense industry, our IMUs have been recognized by clients in more than 35 countries around the globe.
Conclusion
In short, an IMU is a highly advanced tool that delivers crucial motion and orientation data across a wide range of industries. Whether you’re in aerospace, defense, or industrial fields, investing in a top-tier IMU can make all the difference when it comes to accuracy and reliability.
